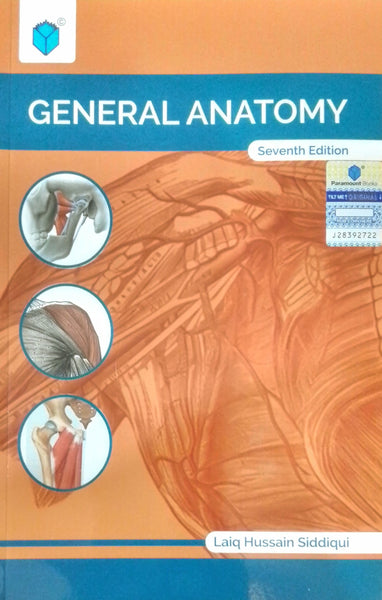
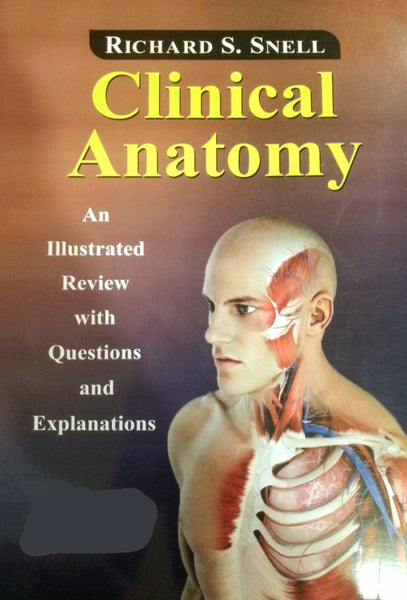
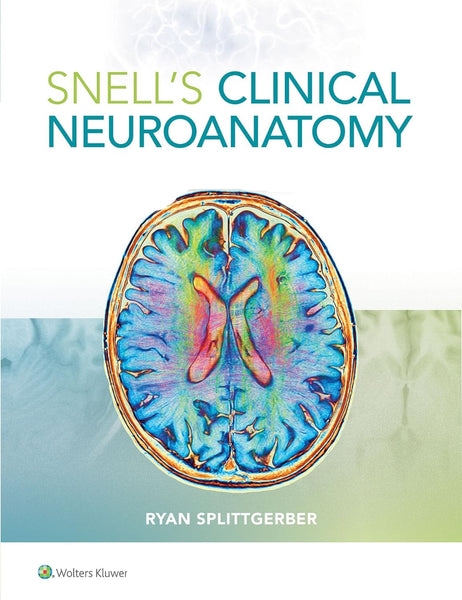
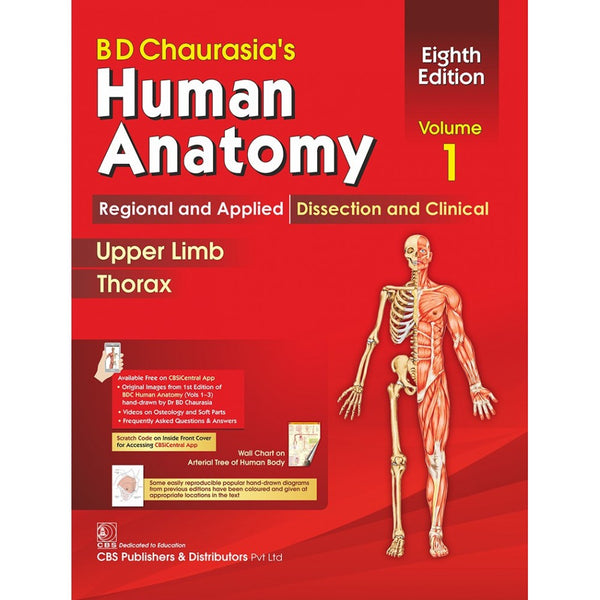
Anatomy Is Fun Part One And Two By Lumbar Plexus
- Publisher: MEDICAL BOOKS
- Availability: In Stock
- SKU: 47584
Rs.1,290.00
Rs.1,495.00
Tags: affordable prices , anatomyeducation , anatomyenthusiasts , best books , best books online , Best Price , best prices , Best Selling Books , best shop , Book Shop , Book shopping , bookshop , bookshop Multan , bookshop near me , bookshop online , bookshop online Multan , bookshopPakistan , buy online books , coma , comaawareness , Convenient Shopping , digital shopping , femoralnerve , good books , good booksonline , healthcare , healthcareprofessionals , innervation , Internet Shop , learningresources , lowerlimb , lumbarplexus , medicalstudents , motor , nervefunction , nerveinjury , nerves , neurological , neuropathy , neuroscience , obturatornerve , occupationaltherapy , one stop shop , Online Book Shop , ONLINE BOOKS , Online Books Shop , online books store , Online Bookshop , Online Bookshop Pakistan , online bookstore , online shop , online shopping , Online Shopping Pakistan , OnlineShoppingPakistan , painmanagement , Pakistan Bookshop , PakistanBookshop , PakistanOnlineShopping , physicaltherapy , price cut , price-friendly Comprehensive , ReasonablePrice , recovery , reduced price , secure shopping , sensory , Shopping , ShopSmartPakistan , surgicaltechniques , Virtual Shop
Anatomy Is Fun Part One And Two By Lumbar Plexus provides an engaging and accessible exploration of human anatomy, specifically focusing on the lumbar plexus. This educational resource aims to make learning about the complexities of the human body enjoyable and comprehensible. Through clear explanations and visual aids, readers can delve into the intricacies of anatomical structures and their functions. From understanding the lumbar plexus to grasping its clinical significance, this resource serves as a valuable tool for students, educators, and enthusiasts alike.
Key Points:
1. Lumbar Plexus Composition: The lumbar plexus is formed by the anterior rami of the first four lumbar nerves (L1-L4), along with contributions from the subcostal nerve (T12). It supplies motor and sensory innervation to the lower abdomen, pelvis, and anterior thigh.
2. Major Branches: Key branches of the lumbar plexus include the femoral nerve, obturator nerve, lateral femoral cutaneous nerve, and iliohypogastric nerve. Each nerve has distinct functions and distributions, contributing to various aspects of lower limb movement and sensation.
3. Femoral Nerve: The femoral nerve is the largest branch of the lumbar plexus and primarily innervates the muscles of the anterior thigh. It also provides sensory innervation to the anterior thigh and medial leg, making it crucial for activities such as walking and standing.
4. Obturator Nerve: Originating from the lumbar plexus, the obturator nerve innervates the muscles of the medial thigh. It plays a vital role in adduction of the thigh and contributes to the sensation in the inner thigh region.
5. Lateral Femoral Cutaneous Nerve: Responsible for providing sensory innervation to the lateral thigh, the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve is a significant branch of the lumbar plexus. Its dysfunction can lead to conditions like meralgia paresthetica, characterized by pain and tingling in the thigh.
6. Iliohypogastric Nerve: The iliohypogastric nerve is involved in providing sensory innervation to the skin over the lower abdomen and the lateral gluteal region. It also supplies motor fibers to the transversus abdominis and internal oblique muscles.
7. Clinical Relevance: Understanding the lumbar plexus is crucial in clinical practice, particularly in diagnosing and treating conditions affecting the lower limbs and pelvic region. Knowledge of its anatomy aids in localizing nerve injuries, planning surgical interventions, and managing neuropathic pain.
8. Nerve Injury: Injuries to the lumbar plexus can result from trauma, surgical complications, or pathological processes. Depending on the affected nerve(s), symptoms may include weakness, sensory deficits, and impaired reflexes, necessitating prompt evaluation and appropriate management.
9. Surgical Considerations: Surgeons operating in the lumbar and pelvic regions must have a thorough understanding of the lumbar plexus anatomy to avoid inadvertent nerve damage. Preoperative assessment and precise surgical techniques help minimize the risk of postoperative complications.
10. Rehabilitation and Recovery: Rehabilitation following lumbar plexus injury or surgery focuses on restoring functional mobility, alleviating pain, and optimizing nerve regeneration. Physical therapy, occupational therapy, and pharmacological interventions play integral roles in facilitating recovery and improving patient outcomes.
Anatomy Is Fun Part One And Two By Lumbar Plexus offers a holistic exploration of the lumbar plexus, blending comprehensive information with interactive learning tools. Whether you're a medical student, healthcare professional, or anatomy enthusiast, this resource serves as a valuable companion in unraveling the mysteries of human anatomy.
════ ⋆★⋆════
Writer ✤ Lumbar Plexus